Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Center for Computational Science & e-Systems
JAEA-Evaluation 2023-001, 38 Pages, 2023/07
Research on advanced computational science for nuclear applications, based on "the plan to achieve the medium- and long-term goal of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency", has been performed by Center for Computational Science & e-Systems (CCSE), Japan Atomic Energy Agency. CCSE established a committee consisting of external experts and authorities which evaluates and advises toward the future research and development. This report summarizes the results of the R&D performed by CCSE in FY2022 (April 1st, 2022 - March 31st, 2023) and their evaluation by the committee.
Center for Computational Science & e-Systems
JAEA-Evaluation 2022-004, 38 Pages, 2022/11
Research on advanced computational science for nuclear applications, based on "the plan to achieve the mid- and long-term goal of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency", has been performed by Center for Computational Science & e-Systems (CCSE), Japan Atomic Energy Agency. CCSE established a committee consisting of external experts and authorities which evaluates and advises toward the future research and development. This report summarizes the results of the R&D performed by CCSE in FY2021 (April 1st, 2021 - March 31st, 2022) and their evaluation by the committee.
Center for Computational Science & e-Systems
JAEA-Evaluation 2022-003, 61 Pages, 2022/11
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (hereinafter referred to as "JAEA") consults an assessment committee, "Evaluation Committee of Research Activities for Computational Science and Technology Research" (hereinafter referred to as "Committee") for result and in-advance evaluation of "Computational Science and Technology Research", in accordance with "General Guideline for the Evaluation of Government Research and Development (R&D) Activities" by Cabinet Office, Government of Japan, "Guideline for Evaluation of R&D in Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology" and "Regulation on Conduct for Evaluation of R&D Activities" by the JAEA. In response to the JAEA's request, the Committee assessed the research program of the Center for Computational Science and e-Systems (hereinafter referred to as "CCSE"). The Committee evaluated the management and research activities of the CCSE based on explanatory documents prepared by the CCSE, and oral presentations with questions-and answers.
Center for Computational Science & e-Systems
JAEA-Evaluation 2021-001, 66 Pages, 2021/11
Research on advanced computational science for nuclear applications, based on "the plan to achieve the mid- and long-term goal of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency", has been performed by Center for Computational Science & e-Systems (CCSE), Japan Atomic Energy Agency. CCSE established a committee consisting of external experts and authorities which does research evaluation and advice for the assistance of the future research and development. This report summarizes the results of the R&D performed by CCSE in FY2020 (April 1st, 2020 - March 31st, 2021), the results expected at the end of the 3rd mid and long-term goal period, and the evaluation by the committee on them.
Ina, Takuya*; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Imamura, Toshiyuki*; Yamashita, Susumu; Onodera, Naoyuki
Proceedings of 12th Workshop on Latest Advances in Scalable Algorithms for Large-Scale Systems ScalA21) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2021/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:48.91(Computer Science, Software Engineering)A new mixed-precision preconditioner based on the iterative refinement (IR) method is developed for preconditioned conjugate gradient (P-CG) and multigrid preconditioned conjugate gradient (MGCG) solvers in a multi-phase thermal-hydraulic CFD code JUPITER. In the IR preconditioner, all data is stored in FP16 to reduce memory access, while all computation is performed in FP32. The hybrid FP16/32 implementation keeps the similar convergence property as FP32, while the computational performance is close to FP16. The developed solvers are optimized on Fugaku (A64FX), and applied to ill-conditioned matrices in JUPITER. The P-CG and MGCG solvers with the new IR preconditioner show excellent strong scaling up to 8,000 nodes, and at 8,000 nodes, they are respectively accelerated up to 4.86 and 2.39
and 2.39 from the conventional ones on Oakforest-PACS (KNL).
from the conventional ones on Oakforest-PACS (KNL).
Center for Computational Science & e-Systems
JAEA-Evaluation 2020-002, 37 Pages, 2020/12
Research on advanced computational science for nuclear applications, based on "the plan to achieve the mid and long term goal of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency", has been performed at Center for Computational Science & e-Systems (CCSE), Japan Atomic Energy Agency. CCSE established a committee consisting of outside experts and authorities which does research evaluation and advice for the assistance of the future research and development. This report summarizes the results of the R&D performed at CCSE in FY2019 (April 1st, 2019 - March 31st, 2020) and the evaluation by the committee on them.
Idomura, Yasuhiro; Ina, Takuya*; Ali, Y.*; Imamura, Toshiyuki*
Proceedings of International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage, and Analysis (SC 2020) (Internet), p.1318 - 1330, 2020/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:36.4(Computer Science, Information Systems)The multi-scale full- simulation of the next generation experimental fusion reactor ITER based on a five dimensional (5D) gyrokinetic model is one of the most computationally demanding problems in fusion science. In this work, a Gyrokinetic Toroidal 5D Eulerian code (GT5D) is accelerated by a new mixed-precision communication-avoiding (CA) Krylov method. The bottleneck of global collective communication on accelerated computing platforms is resolved using a CA Krylov method. In addition, a new FP16 preconditioner, which is designed using the new support for FP16 SIMD operations on A64FX, reduces both the number of iterations (halo data communication) and the computational cost. The performance of the proposed method for ITER size simulations with 0.1 trillion grids on 1,440 CPUs/GPUs on Fugaku and Summit shows 2.8x and 1.9x speedups respectively from the conventional non-CA Krylov method, and excellent strong scaling is obtained up to 5,760 CPUs/GPUs.
simulation of the next generation experimental fusion reactor ITER based on a five dimensional (5D) gyrokinetic model is one of the most computationally demanding problems in fusion science. In this work, a Gyrokinetic Toroidal 5D Eulerian code (GT5D) is accelerated by a new mixed-precision communication-avoiding (CA) Krylov method. The bottleneck of global collective communication on accelerated computing platforms is resolved using a CA Krylov method. In addition, a new FP16 preconditioner, which is designed using the new support for FP16 SIMD operations on A64FX, reduces both the number of iterations (halo data communication) and the computational cost. The performance of the proposed method for ITER size simulations with 0.1 trillion grids on 1,440 CPUs/GPUs on Fugaku and Summit shows 2.8x and 1.9x speedups respectively from the conventional non-CA Krylov method, and excellent strong scaling is obtained up to 5,760 CPUs/GPUs.
Idomura, Yasuhiro; Asahi, Yuichi; Ina, Takuya; Matsuoka, Seikichi
Proceedings of 24th International Congress of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics (ICTAM 2016), p.3106 - 3107, 2016/08
Turbulent transport in fusion plasmas is one of key issues in ITER. To address this issue via the five dimensional (5D) gyrokinetic model, a novel computing technique is developed, and strong scaling of the Gyrokinetic Toroidal 5D Eulerian code GT5D is improved up to 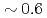 million cores on the K-computer. The computing technique consists of multi-dimensional/multi-layer domain decomposition, overlap of communication and computation, and optimization of computing kernels for multi-core CPUs. The computing power enabled us to study ITER relevant issues such as the plasma size scaling of turbulent transport. Towards the next generation burning plasma turbulence simulations, the physics model is extended including kinetic electrons and multi-species ions, and computing kernels are further optimized for the latest many-core architectures.
million cores on the K-computer. The computing technique consists of multi-dimensional/multi-layer domain decomposition, overlap of communication and computation, and optimization of computing kernels for multi-core CPUs. The computing power enabled us to study ITER relevant issues such as the plasma size scaling of turbulent transport. Towards the next generation burning plasma turbulence simulations, the physics model is extended including kinetic electrons and multi-species ions, and computing kernels are further optimized for the latest many-core architectures.
Nakajima, Norihiro; Nishida, Akemi; Kawakami, Yoshiaki; Suzuki, Yoshio; Sawa, Kazuhiro; Iigaki, Kazuhiko
Proceedings of 23rd International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-23) (DVD-ROM), 5 Pages, 2015/05
A numerical analysis controlling and managing system is implemented on K, which controls the modelling process and data treating, although the manager only controls a structural analysis by finite element method. The modeling process is described by the list of function ID and its procedures in a data base. The manager executes the process by order in the list for simulation procedures. The manager controls the intention of an analysis by changing the analytical process one to another. Experiments were carried out with static and dynamic analyses.
Furuta, Takuya; Sato, Tatsuhiko
Igaku Butsuri, 35(3), p.264 - 268, 2015/00
Time-consuming Monte Carlo dose calculation becomes feasible owing to the development of computer technology. However, the recent development is due to emergence of the multi-core high performance computers. Therefore, parallel computing becomes a key to achieve good performance of software programs. A Monte Carlo simulation code PHITS contains two parallel computing functions, the distributed-memory parallelization using protocols of MPI and the shared-memory parallelization using OpenMP directives. Users can choose the two functions according to their needs. This paper gives the explanation of the two functions with their advantages and disadvantages. Some test applications are also provided to show their performance using a typical multi-core high performance workstation.
Nakajima, Norihiro; Nishida, Akemi; Kawakami, Yoshiaki; Suzuki, Yoshio
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Dai-24-Kai Sekkei Kogaku, Shisutemu Bumon Koenkai Koen Rombunshu (USB Flash Drive), 9 Pages, 2014/09
In this paper, a numerical analysis's controlling and managing system is suggested, which controls the modelling process and data treating for structural robustness, although a numerical analysis's manager only controls a structural analysis by finite element method. The modeling process is described by the list of function ID and its procedures in a data base. The analytical modeling manager executes the process by order of the lists for simulation procedures. The manager controls the intention of an analysis by changing the analytical process one to another. Modeling process was experimentally found that may subject to the intention of designing index. In the numerical experiments, K, supercomputer is utilized by using parallel computing resource with the controlling and managing system.
Takeshima, Yuriko; Suzuki, Yoshio*; Matsumoto, Nobuko*; Sai, Kazunori*; Nakajima, Norihiro
Proceedings of 4th International Symposium on Advanced Fluid Information and Transdiciplinary Fluid Integration (AFI/TFI 2004), p.157 - 158, 2004/11
The Information-Technology-Based Laboratory (ITBL) project aims to construct a virtual research environment which shares intellectual resources such as the super computers by the grid computing, softwares and data in Japan and supports joint researches at a distance. In the project, two visualization systems: the PATRAS/ITBL and the AVS/ITBL have been developed. The feature of the PATRAS/ITBL is the collaborative, real-time visualization of data resulting from an execution of numerical simulations. The AVS/ITBL visualization system enables remote postprocessing visualization of any data stored on any supercomputer located in the ITBL network. The global structure and technologies of these systems are presented.
Nakajima, Norihiro; Ono, Nobuaki*; Suzuki, Yoshio*; Kureta, Masatoshi*
Denki Gakkai Rombunshi, C, 124(10), p.2197 - 2198, 2004/10
Our research interest is to implement volume rendering on CAVE system at enough frame rate. It can be implemented on CAVE easily using texture mapping but there are some defects; for example frame rate declines when the view point is close to the data and images projected to the screens become big. Thus we try to find another way to implement it on CAVE. Considering that Onyx300 is a parallel computer and there are some algorisms of volume rendering which improve the frame rate, we make the program that draws stereo images through two of the algorisms and by parallel computing, and displays only two images on CAVE. And we confirm that this program works well and draws stereo images at sufficient frame rates.
Nakajima, Norihiro
Keisan Kogaku, 9(2), p.919 - 920, 2004/04
Comopuational environment is introduced in Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute. A mission of Center for Promotion of Computational Science and Engineering is also introduced and discussed the research and development theme. As next generation comopuational environment, ITBL as a grid computing system is summarized.
Ueshima, Yutaka
JAERI-Conf 2004-003, 62 Pages, 2004/03
no abstracts in English
Advanced Photon Research Center; Center for Promotion of Computational Science and Engineering
JAERI-Conf 2004-002, 81 Pages, 2004/03
no abstracts in English
Suzuki, Yoshio
JAERI-Conf 2004-003, p.52 - 55, 2004/03
no abstracts in English
Isogai, Kentaro*
JAERI-Data/Code 2003-010, 28 Pages, 2003/08
In these days, a large scale simulation by supercomputers has been prevailent in various fields of research and development. In such computations, however, there may be an excessively needless amount of work for researchers. This is due to such various facts such as that due to the development of high performance of supercomputers, too much data or too large a variety of data have become possible to treat, or the management of input or output data has become inadequate or improper in circumstances such as setting the environment of input parameters, missing computational results, and information processing which are common experiences among researchers.Therefore, we have been engaged in the construction of an integrated management system of input & output data in supporting a distributed computational system for large scale simulations for a variety of researchers as a common utility. In this article, the introduction of the distributed computing system, especially the explanation of the control server in it is described.
Suzuki, Yoshio; Sai, Kazunori*; Matsumoto, Nobuko*; Hazama, Osamu
IEEE Computer Graphics and Applications, 23(2), p.32 - 39, 2003/04
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:51.96(Computer Science, Software Engineering)Visualization systems PATRAS/ITBL and AVS/ITBL, which are based on visualization software PATRAS and AVS/Express respectively, have been developed on a global, heterogeneous computing environment, called Information Technology Based Laboratory (ITBL). PATRAS/ITBL allows for real-time visualization of the numerical results acquired from coupled multi-physics numerical simulations, executed on different hosts situated in remote locations. A collaborative visualization among numerous sites for this type of simulation was also made possible. AVS/ITBL allows for post processing visualization. The scientific data located in remote sites may be selected and visualized on web browser installed in a user terminal. The global structure and main functions of these systems are presented.
Idomura, Yasuhiro; Tokuda, Shinji; Kishimoto, Yasuaki
Nuclear Fusion, 43(4), p.234 - 243, 2003/04
Times Cited Count:119 Percentile:94.96(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English